NOW APPROVED IN TABLET FORMULATION: AVAILABLE EARLY OCTOBER 2025
CONSISTENT SAFETY ACROSS LINES OF THERAPY, INCLUDING LOW RATES OF CARDIAC EVENTS IN 1L AND 2L CLL
COHORT 1: OVERALL INCIDENCE OF ADVERSE REACTIONS (ARs)*1,2
| Adverse Reactions | ARs in ≥10% of Patients Without Del(17p) | Pooled Safety Population† | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BRUKINSA (n=240) | BR (n=227) | BRUKINSA (N=1729) | ||||
| All Grades (%) | Grade ≥3 (%) | All Grades (%) | Grade ≥3 (%) | All Grades (%) | Grade ≥3 (%) | |
| Musculoskeletal pain | 33 | 2 | 17 | 0.4 | 24 | 2 |
| Upper respiratory tract infection | 28 | 1 | 15 | 0.9 | 38 | 3 |
| Pneumonia | 13‡ | 5 | 8§ | 4 | 17 | 11 |
| Hemorrhage | 27‡ | 4 | 4 | 0.4 | 32 | 4 |
| Hypertension | 14 | 7 | 5 | 3 | 14 | 7 |
| Rash | 24 | 1 | 30 | 5 | 25 | 0.6 |
| Bruising | 24 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 21 | 0.1 |
| Cough | 15 | 0 | 10 | 0 | 20 | 0.1 |
| Diarrhea | 14 | 0.8 | 12§ | 0.9 | 20 | 2 |
| Constipation | 10 | 0.4 | 18 | 0 | 13 | 0.3 |
| Nausea | 10 | 0 | 33 | 1 | 11 | 0.2 |
| Fatigue | 14 | 1 | 21 | 2 | 18 | 1 |
| Second primary malignancy | 13‡ | 6 | 1 | 0.4 | 15 | 7 |
| Headache | 12 | 0 | 8 | 0 | 11 | 0.3 |
| Dizziness | 11 | 0.8 | 5 | 0 | 11 | 0.3 |
*Median duration of exposure was 26.1 months for BRUKINSA and 5.6 months for BR in Cohort 1.3
†Includes chronic lymphocytic leukemia, Waldenström’s macroglobulinemia, mantle cell lymphoma, follicular lymphoma, marginal zone lymphoma, hairy cell leukemia, diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, and Richter’s transformation.2
‡Includes 3 fatal outcomes.1
§Includes 2 fatal outcomes.1
Adverse reactions at ~5 years reported in ≥10% of patients (BRUKINSA vs BR, respectively) in the SEQUOIA trial (Cohort 1) included: COVID-19 (39% vs 12%), contusion (22% vs 4%), diarrhea (21% vs 14%), upper respiratory tract infection (20% vs 14%), hypertension (20% vs 12%), arthralgia (19% vs 11%), fatigue (18% vs 18%), cough (16% vs 11%), rash (14% vs 20%), nausea (14% vs 33%), constipation (14% vs 19%), pneumonia (14% vs 11%), neutropenia (13% vs 46%), vomiting (13% vs 15%), urinary tract infection (13% vs 10%), headache (12% vs 11%), back pain (12% vs 8%), pyrexia (11% vs 27%), edema peripheral (11% vs 9%), dizziness (11% vs 5%), pain in extremity (11% vs 7%), pruritus (10% vs 8%).4
Median duration of exposure at ~5 years was 60.5 months for BRUKINSA and 5.6 months for BR.4
COHORT 2: OVERALL INCIDENCE OF ARs*1,2
| Adverse Reactions | ARs in ≥10% of Patients With Del(17p) | Pooled Safety Population† | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BRUKINSA (n=111) | BRUKINSA (N=1729) | |||
| All Grades (%) | Grade ≥3 (%) | All Grades (%) | Grade ≥3 (%) | |
| Upper respiratory tract infection | 38 | 0 | 38 | 3 |
| Pneumonia | 20‡ | 8 | 17 | 11 |
| Musculoskeletal pain | 38 | 3 | 24 | 2 |
| Rash | 28 | 0 | 25 | 0.6 |
| Bruising | 26 | 0.9 | 21 | 0.1 |
| Hemorrhage | 28 | 5 | 32 | 4 |
| Hypertension | 11 | 5 | 14 | 7 |
| Second primary malignancy | 22§ | 6 | 15 | 7 |
| Diarrhea | 18 | 0.9 | 20 | 2 |
| Nausea | 16 | 0 | 11 | 0.2 |
| Constipation | 15 | 0 | 13 | 0.3 |
| Abdominal pain | 12 | 2 | 11 | 0.9 |
| Cough | 18 | 0 | 20 | 0.1 |
| Dyspnea | 13 | 0 | 8 | 0.6 |
| Fatigue | 14 | 0.9 | 18 | 1 |
| Headache | 11 | 2 | 11 | 0.3 |
*Median duration of exposure was 30 months in Cohort 2.3
†Includes chronic lymphocytic leukemia, Waldenström’s macroglobulinemia, mantle cell lymphoma, follicular lymphoma, marginal zone lymphoma, hairy cell leukemia, diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, and Richter’s transformation.2
‡Includes 1 fatal outcome.1
§Includes non-melanoma skin cancer in 13%.1
Adverse reactions at ~5 years reported in ≥15% of BRUKINSA patients in the SEQUOIA trial (Cohort 2) included: COVID-19 (33%), upper respiratory tract infection (28%), arthralgia (26%), diarrhea (22%), contusion (22%), back pain (19%), constipation (19%), nausea (18%), cough (18%), basal cell carcinoma (17%), rash (17%), fall (17%), hypertension (16%), urinary tract infection (16%), and pneumonia (15%).5
Median follow-up was 65.8 months.5
There were no new safety signals at ~5 years with BRUKINSA4
| Laboratory Abnormality | Cohort 1: Patients Without Del(17p) | Cohort 2: Patients With Del(17p) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BRUKINSA (n=239)† | BR (n=227)† | BRUKINSA (n=111)‡ | ||||
| All Grades (%) | Grade ≥3 (%) | All Grades (%) | Grade ≥3 (%) | All Grades (%) | Grade ≥3 (%) | |
| Neutrophils decreased | 37 | 15 | 80 | 53 | 42 | 19§ |
| Hemoglobin decreased | 29 | 3 | 66 | 8 | 26 | 4 |
| Platelets decreased | 27 | 2 | 61 | 11 | 23 | 0.9 |
| Leukocytes increased | 21¶ | 21 | 0.4 | 0.4 | NR | NR |
| Glucose increased# | 55 | 7 | 67 | 10 | 52 | 6 |
| Creatinine increased | 22 | 0.8 | 18 | 0.4 | 27 | 0.9 |
| Magnesium increased | 22 | 0 | 14 | 0.4 | 31 | 0 |
| Alanine aminotransferase increased | 21 | 2 | 23 | 2 | NR | NR |
*Median duration of exposure was 26.1 months for BRUKINSA and 5.6 months for BR in Cohort 1, and 30 months for BRUKINSA in Cohort 2.3
†In Cohort 1, the denominator used to calculate the rate was 239 in the BRUKINSA arm and 227 in the BR arm, based on the number of patients with a baseline value and at least 1 post-treatment value. Grading is based on NCI CTCAE criteria.1
‡In Cohort 2, the denominator used to calculate the rate varied from 110 to 111 based on the number of patients with a baseline value and at least 1 post-treatment value. Grading is based on NCI CTCAE criteria.1
§Grade 4, 9%.1
¶Lymphocytes increased in 15%.1
#Patients on study were not required to fast for lab tests.1
| Adverse Events | SEQUOIA | Pooled Safety Population† | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BRUKINSA (n=240) | BR (n=227) | BRUKINSA (N=1729) | ||||
| All Grades (%) | Grade ≥3 (%) | All Grades (%) | Grade ≥3 (%) | All Grades (%) | Grade ≥3 (%) | |
| Fatigue | 12 | 1 | 15 | 0.9 | 18 | 1 |
| Headache | 11 | 0 | 7 | 0 | 11 | 0.3 |
| Myalgia | 4 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 4 | 0.3 |
| Arthralgia | 13 | 0.8 | 9 | 0.4 | 14 | 0.6 |
| Atrial fibrillation/flutter | 3 | 0.4 | 3 | 1 | 4 | 2 |
| Hypertension | 14 | 6 | 11 | 5 | 14 | 7 |
| Major bleeding‡ | 5 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 5 | 4 |
*Median duration of exposure was 26.1 months for BRUKINSA and 5.6 months for BR in Cohort 1.3
†Includes chronic lymphocytic leukemia, Waldenström’s macroglobulinemia, mantle cell lymphoma, follicular lymphoma, marginal zone lymphoma, hairy cell leukemia, diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, and Richter’s transformation.2
‡In SEQUOIA, major bleeding included subdural hematoma and subdural hemorrhage.3
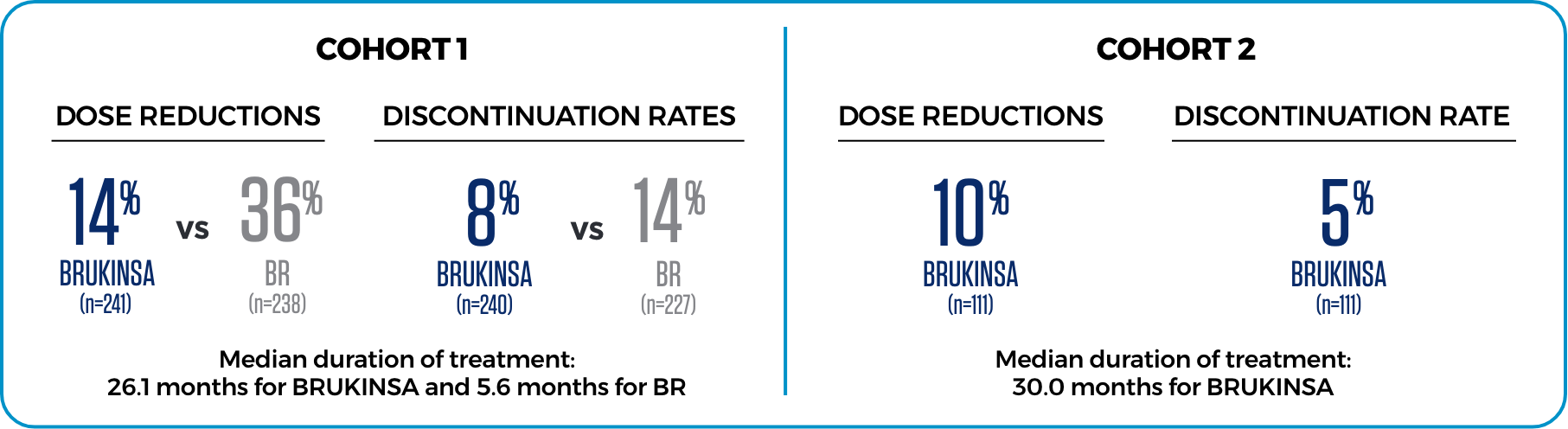
LOWER RATES OF DOSE REDUCTIONS AND DISCONTINUATION DUE TO AEs3
LOW RATES OF AFIB IN PATIENTS WITHOUT DEL(17p) AT THE INITIAL ANALYSIS3
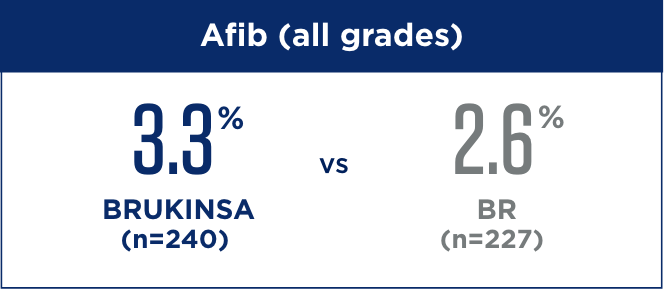
- Grade ≥3 rate of afib was 0.4% with BRUKINSA vs 1.3% with BR
Rates of afib remained consistent at the ~5-year milestone4
Median duration of treatment at the initial analysis in Cohort 1 was 26.1 months for BRUKINSA and 5.6 months for BR; in Cohort 2 it was 30 months for BRUKINSA.3
1L=first line; 2L=second line; afib=atrial fibrillation; BR=bendamustine+rituximab; CLL=chronic lymphocytic leukemia; NCI CTCAE=National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events; NR=not reported.
| Adverse Reactions | ARs in ≥10% of Patients | Pooled Safety Population† | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BRUKINSA (n=324) | Ibrutinib (n=324) | BRUKINSA (N=1729) | ||||
| All Grades (%) | Grade ≥3 (%) | All Grades (%) | Grade ≥3 (%) | All Grades (%) | Grade ≥3 (%) | |
| Upper respiratory tract infection | 27 | 1 | 22 | 1 | 38 | 3 |
| Pneumonia | 18‡ | 9 | 19§ | 11 | 17 | 11 |
| COVID-19 | 14‡ | 7 | 10§ | 5 | 10 | 5 |
| Musculoskeletal pain | 26 | 0.6 | 28 | 0.6 | 24 | 2 |
| Hemorrhage | 24‡ | 3 | 26§ | 4 | 32 | 4 |
| Hypertension | 19 | 13 | 20 | 13 | 14 | 7 |
| Rash | 20 | 1 | 21 | 0.9 | 25 | 0.6 |
| Bruising | 16 | 0 | 14 | 0 | 21 | 0.1 |
| Diarrhea | 14 | 2 | 22 | 0.9 | 20 | 2 |
| Fatigue | 13 | 0.9 | 14 | 0.9 | 18 | 1 |
| Cough | 11 | 0.3 | 11 | 0 | 20 | 0.1 |
| Dizziness | 10 | 0 | 7 | 0 | 11 | 0.3 |
Rates of hypertension were comparable between BRUKINSA and ibrutinib1
- A medical history of hypertension was reported in more than half of these patient events for both BRUKINSA and ibrutinib2
*Median duration of exposure was 28.4 months for BRUKINSA and 24.3 months for ibrutinib.6
†Includes chronic lymphocytic leukemia, Waldenström’s macroglobulinemia, mantle cell lymphoma, follicular lymphoma, marginal zone lymphoma, hairy cell leukemia, diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, and Richter’s transformation.2
‡Includes fatal outcomes: pneumonia (9 patients), COVID-19 (8 patients), and hemorrhage (1 patient).1
§Includes fatal outcomes: pneumonia (10 patients), COVID-19 (9 patients), and hemorrhage (2 patients).1
Adverse events at ~3.5 years reported in ≥10% of patients (BRUKINSA vs ibrutinib, respectively) in the ALPINE trial included: COVID-19 (46% vs 33%), neutropenia (32% vs 30%), upper respiratory tract infection (29% vs 20%), hypertension (27% vs 25%), diarrhea (19% vs 26%), arthralgia (17% vs 19%), anemia (17% vs 19%), pneumonia (15% vs 17%), contusion (15% vs 12%), and fatigue (11% vs 15%).7
Median duration of exposure at ~3.5 years was 41.2 months for BRUKINSA and 37.8 months for ibrutinib.7
There were no new safety signals at ~3.5 years with BRUKINSA7
| Laboratory Abnormality | BRUKINSA (n=321) | Ibrutinib (n=321)† | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All Grades (%) | Grade ≥3 (%) | All Grades (%) | Grade ≥3 (%) | |
| Neutrophils decreased | 43 | 15 | 33 | 16 |
| Hemoglobin decreased | 28 | 4 | 32 | 4 |
| Lymphocytes increased | 24 | 19 | 26 | 19 |
| Platelets decreased | 22 | 4 | 24 | 3 |
| Glucose increased‡ | 52 | 5 | 29 | 3 |
| Creatinine increased | 26 | 0 | 23 | 0 |
| Phosphate decreased | 21 | 3 | 13 | 2 |
| Calcium decreased | 21 | 0.6 | 29 | 0 |
*Median duration of exposure was 28.4 months for BRUKINSA and 24.3 months for ibrutinib.6
†The denominator used to calculate rates of lab abnormalities varied from 320 to 321 in the ibrutinib arm based on the number of patients with a baseline value and at least 1 post-treatment value. Grading is based on NCI CTCAE criteria.
‡Patients on study were not required to fast for lab tests.
all grades
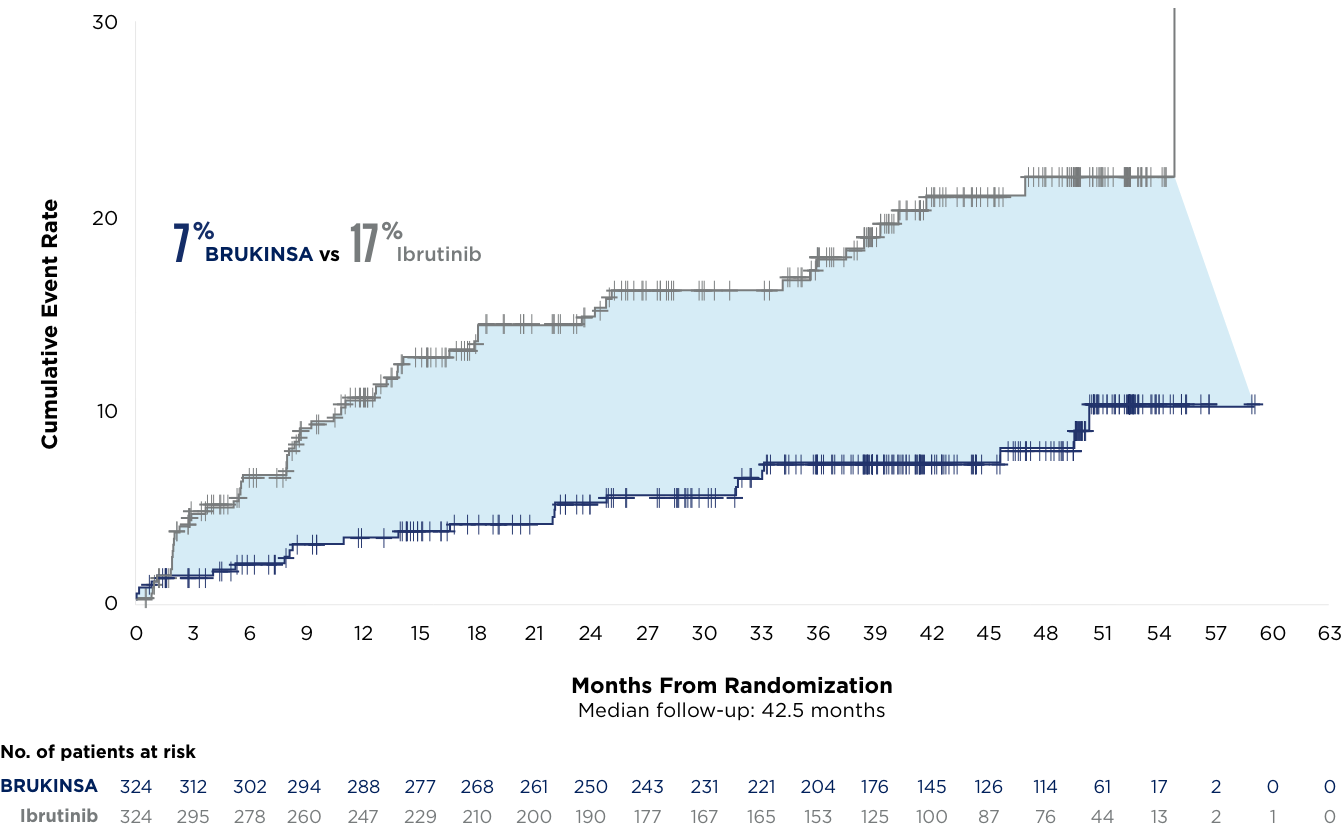
*Median duration of treatment: 28.4 months in the initial analysis and 41.2 months in the milestone analysis.6,7
| Cardiac AEs | Initial Analysis6,8 | ~3.5-Year Milestone7 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BRUKINSA (n=324) | Ibrutinib (n=324) | BRUKINSA (n=324) | Ibrutinib (n=324) | |
| Cardiac AEs | 69 (21%) | 96 (30%) | 84 (26%) | 115 (36%) |
| Serious cardiac AEs | 6 (2%) | 25 (8%) | 13 (4%) | 32 (10%) |
| Cardiac AEs leading to treatment discontinuation | 1 (0.3%)* | 14 (4%)† | 3 (0.9%)‡ | 16 (5%)§ |
| Fatal cardiac AEs | 0 (0%) | 6 (2%) | 0 (0%) | 6 (2%) |
6 cardiovascular (CV) deaths occurred with ibrutinib in patients with and without a history of CV risk
No deaths occurred with BRUKINSA6,7
- Early onset death: 3 of the fatal cardiac events occured within 4 months after initiation of ibrutinib in patients with coexisting cardiac conditions
- Late onset death: 3 of the fatal cardiac events occurred 2-3 years after the initiation of ibrutinib, including in 1 patient who had no history of cardiac disorders
*BRUKINSA cardiac-related discontinuation in 1 patient was for ventricular extrasystoles.6
†Ibrutinib cardiac-related discontinuations were for atrial fibrillation (5), cardiac arrest (2), cardiac failure (2), cardiac failure acute (1), congestive cardiomyopathy (1), myocardial infarction (1), palpitations (1), and ventricular fibrillation (1).6
‡Cardiac AEs leading to treatment discontinuation included ventricular extrasystoles, atrial fibrillation/flutter, and cardiac failure for BRUKINSA.7
§Cardiac AEs leading to treatment discontinuation included atrial fibrillation/flutter, cardiac arrest, cardiac failure, cardiac failure acute, congestive cardiomyopathy, myocardial infarction, palpitations, and ventricular fibrillation for ibrutinib.7
| Adverse Reactions | ALPINE | Pooled Safety Population† | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BRUKINSA (n=324) | Ibrutinib (n=324) | BRUKINSA (N=1729) | ||||
| All Grades (%) | Grade ≥3 (%) | All Grades (%) | Grade ≥3 (%) | All Grades (%) | Grade ≥3 (%) | |
| Fatigue | 13 | 0.9 | 14 | 0.9 | 18 | 1 |
| Headache | 8 | 0 | 9 | 0 | 11 | 0.3 |
| Myalgia | 3 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 4 | 0.3 |
| Arthralgia | 14 | 0 | 15 | 0.3 | 14 | 0.6 |
| Atrial fibrillation and flutter | 5 | 3 | 13 | 4 | 4 | 2 |
| Hypertension | 19 | 13 | 20 | 13 | 14 | 7 |
| Major hemorrhage‡ | 4 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 | 4 |
*Median duration of exposure was 28.4 months for BRUKINSA and 24.3 months for ibrutinib.6
†Includes chronic lymphocytic leukemia, Waldenström’s macroglobulinemia, mantle cell lymphoma, follicular lymphoma, marginal zone lymphoma, hairy cell leukemia, diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, and Richter’s transformation.2
‡Hematuria was the most common major hemorrhage.2

1 patient in the BRUKINSA arm discontinued treatment due to a cardiac AE vs 14 patients in the ibrutinib arm*6
*BRUKINSA cardiac-related discontinuation in 1 patient was for ventricular extrasystoles. Ibrutinib cardiac-related discontinuations were for atrial fibrillation (5), cardiac arrest (2), cardiac failure (2), cardiac failure acute (1), congestive cardiomyopathy (1), myocardial infarction (1), palpitations (1), and ventricular fibrillation (1).6
2L=second line; afib=atrial fibrillation; COVID-19=coronavirus disease 2019; NCI CTCAE=National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events.
Dr Anthony Nguyen discusses the safety profile of BRUKINSA vs ibrutinib in CLL
WATCH OTHER EXPERT OVERVIEWSIMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
What should I tell my healthcare provider before taking BRUKINSA?
Before taking BRUKINSA, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
- have bleeding problems.
- have had recent surgery or plan to have surgery. Your healthcare provider may stop BRUKINSA for any planned medical, surgical, or dental procedure.
- have an infection.
- have or had heart rhythm problems.
- have high blood pressure.
- have liver problems, including a history of hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection.
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. BRUKINSA can harm your unborn baby. If you are able to become pregnant, your healthcare provider may do a pregnancy test before starting treatment with BRUKINSA.
- Females should avoid getting pregnant during treatment and for 1 week after the last dose of BRUKINSA. You should use effective birth control (contraception) during treatment and for 1 week after the last dose of BRUKINSA.
- Males should avoid getting female partners pregnant during treatment and for 1 week after the last dose of BRUKINSA. You should use effective birth control (contraception) during treatment and for 1 week after the last dose of BRUKINSA.
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. It is not known if BRUKINSA passes into your breast milk. Do not breastfeed during treatment with BRUKINSA and for 2 weeks after the last dose of BRUKINSA.
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. Taking BRUKINSA with certain other medications may affect how BRUKINSA works and can cause side effects.
What are the possible side effects of BRUKINSA?
BRUKINSA may cause serious side effects, including:
- Bleeding problems (hemorrhage). Bleeding problems are common with BRUKINSA, and can be serious and may lead to death. Your risk of bleeding may increase if you are also taking a blood thinner medicine. Tell your healthcare provider if you have any signs or symptoms of bleeding, including:
- blood in your stools or black stools (looks like tar)
- pink or brown urine
- unexpected bleeding, or bleeding that is severe or you cannot control
- vomit blood or vomit that looks like coffee grounds
- cough up blood or blood clots
- increased bruising
- dizziness
- weakness
- confusion
- change in speech
- headache that lasts a long time
- Infections that can be serious and may lead to death. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you have fever, chills, or flu-like symptoms.
- Decrease in blood cell counts (white blood cells, platelets, and red blood cells). Your healthcare provider should do blood tests during treatment with BRUKINSA to check your blood counts.
- Second primary cancers. New cancers have happened in people during treatment with BRUKINSA, including cancers of the skin or other organs. Your healthcare provider will check you for other cancers during treatment with BRUKINSA. Use sun protection when you are outside in sunlight.
- Heart rhythm problems (atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter, and ventricular arrhythmias) that can be serious and may lead to death. Tell your healthcare provider if you have any of the following signs or symptoms:
- your heartbeat is fast or irregular
- feel lightheaded or dizzy
- pass out (faint)
- shortness of breath
- chest discomfort
- Liver problems. Liver problems, which may be severe or life-threatening, or lead to death, can happen in people treated with BRUKINSA. Your healthcare provider will do blood tests to check your liver before and during treatment with BRUKINSA. Tell your healthcare provider or get medical help right away if you have any signs of liver problems, including stomach pain or discomfort, dark-colored urine, or yellow skin and eyes.
The most common side effects of BRUKINSA include:
- decreased white blood cell count
- decreased platelet count
- upper respiratory tract infection
- bleeding
- muscle, bone, or joint pain
These are not all the possible side effects of BRUKINSA. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
What is BRUKINSA?
BRUKINSA is a prescription medicine used to treat adults with:
- Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) or small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL).
- Waldenström’s macroglobulinemia (WM).
- Mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) who have received at least one prior treatment for their cancer.
- Marginal zone lymphoma (MZL) when the disease has come back or did not respond to treatment and who have received at least one certain type of treatment.
- Follicular lymphoma (FL), in combination with the medicine obinutuzumab, when the disease has come back or did not respond to treatment and who have received at least two prior treatments.
It is not known if BRUKINSA is safe and effective in children.
Please see full Prescribing Information including Patient Information.

